Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J. Microbiol > Volume 63(1); 2025 > Article
-
Full article
PneusPage: A WEB-BASED TOOL for the analysis of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data of Streptococcus pneumonia -
Eunju Hong1,†, Youngjin Shin2,†, Hyunseong Kim1, Woo Young Cho3, Woo-Hyun Song1, Seung-Hyun Jung4,5
 , Minho Lee1
, Minho Lee1
-
Journal of Microbiology 2025;63(1):e.2409020.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.71150/jm.2409020
Published online: January 24, 2025
1Department of Life Science, Dongguk University-Seoul, Goyang 10326, Republic of Korea
2Basic Medical Science Facilitation Program, Catholic Medical Center, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Republic of Korea
3ConnectaGen, Hanam 12918, Republic of Korea
4Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Republic of Korea
5Integrated Research Center for Genomic Polymorphism, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 06591, Republic of Korea
- Seung-Hyun Jung hyun@catholic.ac.kr Minho Lee MinhoLee@dgu.edu
- †These authors contributed equally to this work
© The Microbiological Society of Korea
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
- With the advent of whole-genome sequencing, opportunities to investigate the population structure, transmission patterns, antimicrobial resistance profiles, and virulence determinants of Streptococcus pneumoniae at high resolution have been increasingly expanding. Consequently, a user-friendly bioinformatics tool is needed to automate the analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae whole-genome sequencing data, summarize clinically relevant genomic features, and further guide treatment options. Here, we developed PneusPage, a web-based tool that integrates functions for species prediction, molecular typing, drug resistance determination, and data visualization of Streptococcus pneumoniae. To evaluate the performance of PneusPage, we analyzed 80 pneumococcal genomes with different serotypes from the Global Pneumococcal Sequencing Project and compared the results with those from another platform, PathogenWatch. We observed a high concordance between the two platforms in terms of serotypes (100% concordance rate), multilocus sequence typing (100% concordance rate), penicillin-binding protein typing (88.8% concordance rate), and the Global Pneumococcal Sequencing Clusters (98.8% concordance rate). In addition, PneusPage offers integrated analysis functions for the detection of virulence and mobile genetic elements that are not provided by previous platforms. By automating the analysis pipeline, PneusPage makes whole-genome sequencing data more accessible to non-specialist users, including microbiologists, epidemiologists, and clinicians, thereby enhancing the utility of whole-genome sequencing in both research and clinical settings. PneusPage is available at https://pneuspage.minholee.net/.
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Results and Discussion
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by supported by KREONET (Korea Research Environment Open NETwork) which is managed and operated by KISTI (Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information), a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2022R1A2C2093050), and a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project grant through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea (HI22C0117). The authors also thank Gunhee Lee and Jonghwan Yoon for suggestions and developmental discussions.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical Statements
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of The Catholic University of Korea (MC22SNSI0058).
Supplementary Information
Table S1.
Table S2.
Table S3.
Table S4.
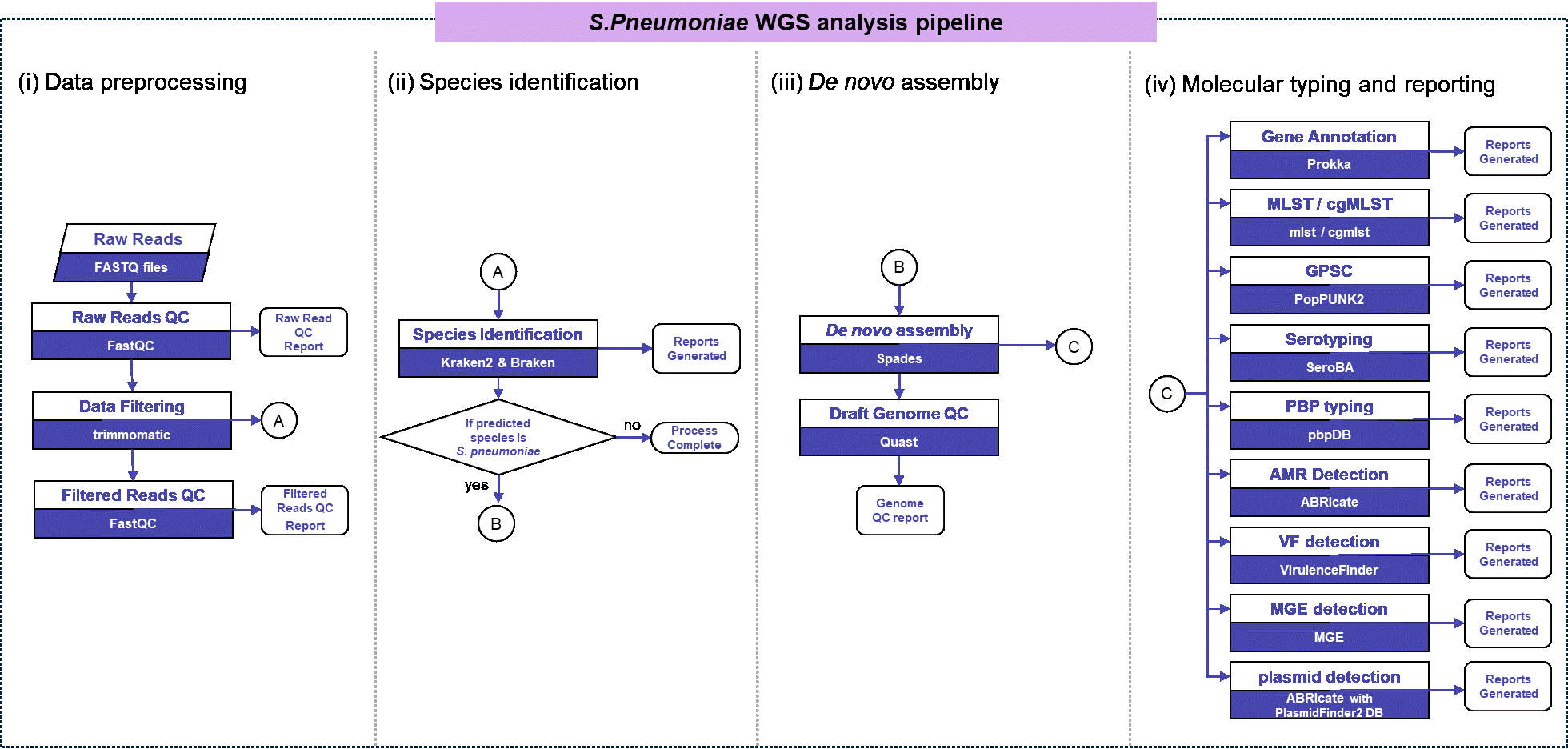
S. pneumoniae WGS analysis pipeline.
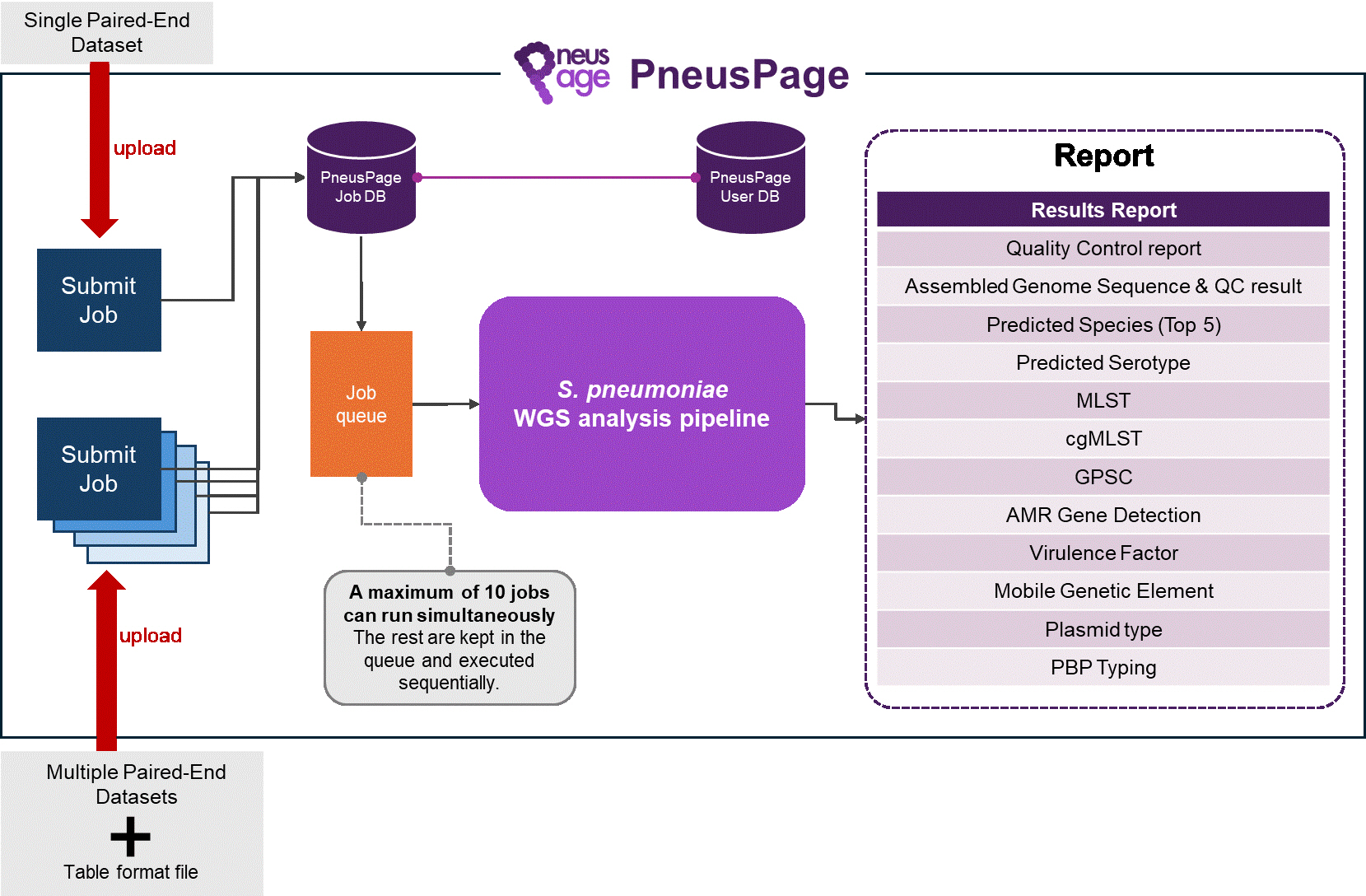
PneusPage web service structure.
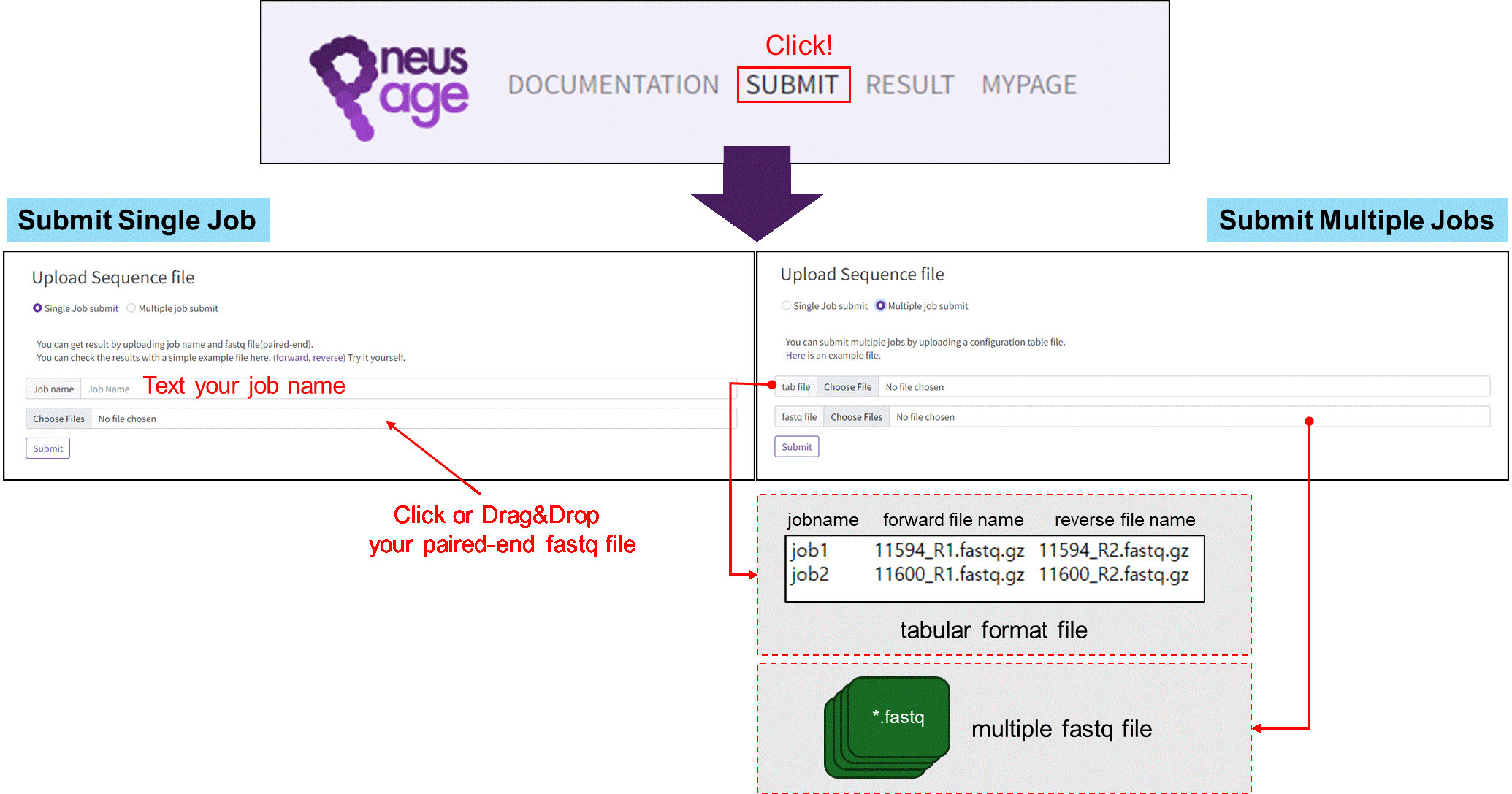
Submitting a job in PneusPage.
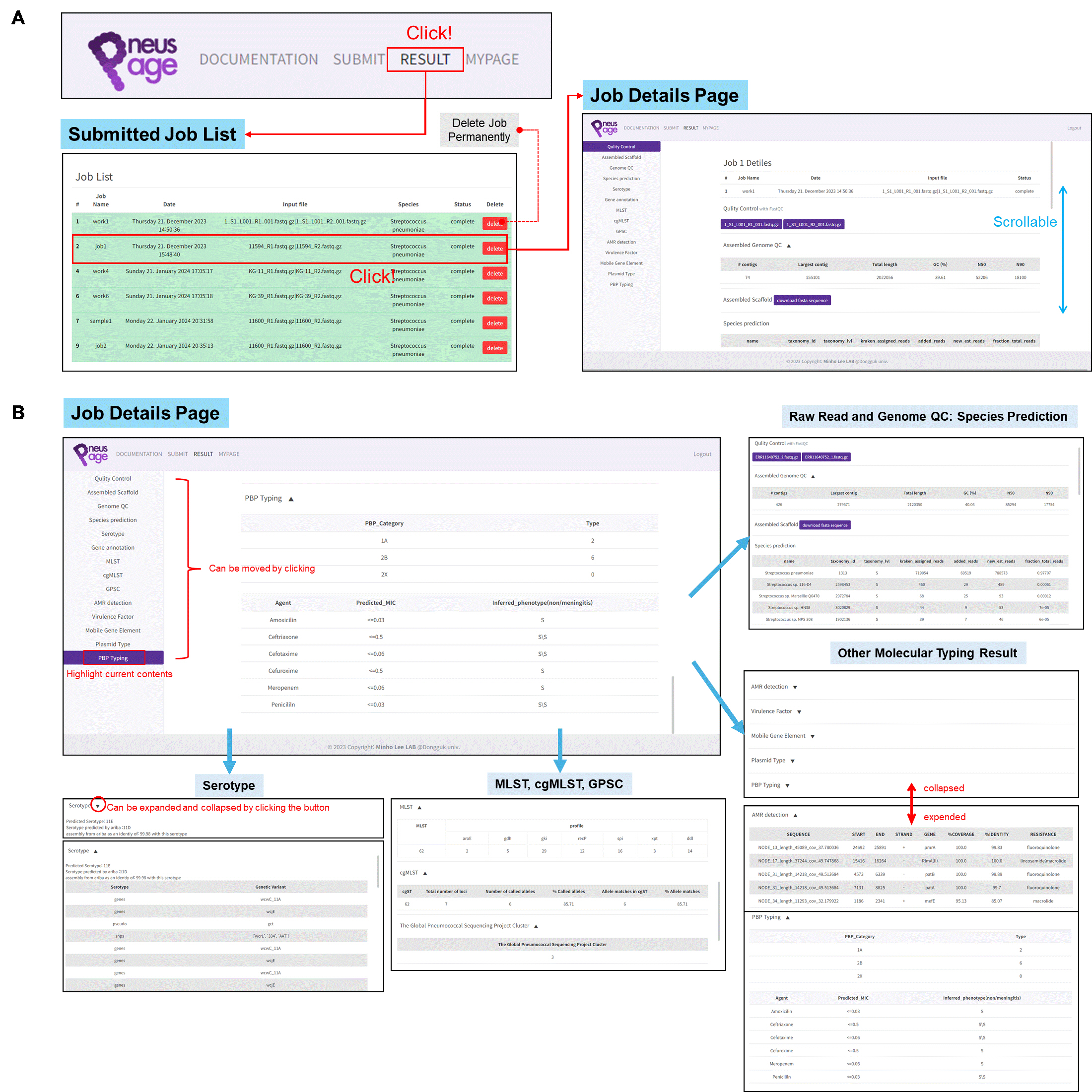
Viewing the Analysis Report in PneusPage.
This table presents the concordance rates between the GPS project database samples and two analysis platform, PathogenWatch and PneusPage, across four key S. pneumoniae typing categories: Serotype, MLST, GPSC, and PBP Typing. The MLST is divided into seven housekeeping genes and sequence type. The PBP typing is subdivided into three specific penicillin-binding proteins and their combination. Concordance percentages are shown between the GPS project dataset and each tools, as well as between the PathogenWatch and PneusPage.
- Alcock BP, Raphenya AR, Lau TTY, Tsang KK, Bouchard M, et al. 2020. CARD 2020: Antibiotic resistome surveillance with the comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Nucleic Acids Res. 48(D1): D517–D525. ArticlePubMed
- Bard JD, Lee F. 2018. Why can't we just use PCR? The role of genotypic versus phenotypic testing for antimicrobial resistance testing. Clin Microbiol Newsl. 40(11): 87–95. ArticlePubMedPMC
- Belman S, Lefrancq N, Nzenze S, Downs S, du Plessis M, et al. 2024. Geographical migration and fitness dynamics of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Nature. 631: 386–392. ArticlePubMedPMC
- Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B. 2014. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics. 30(15): 2114–2120. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- Chang B, Morita M, Lee KI, Ohnishi M. 2018. Whole-genome sequence analysis of streptococcus pneumoniae strains that cause hospital-acquired pneumonia infections. J Clin Microbiol. 56(5): e01822–17. ArticlePubMedPMCLink
- Clausen P, Aarestrup FM, Lund O. 2018. Rapid and precise alignment of raw reads against redundant databases with KMA. BMC Bioinformatics. 19(1): 307.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- Cremers AJH, Mobegi FM, van der Gaast-de Jongh C, van Weert M, van Opzeeland FJ, et al. 2019. The contribution of genetic variation of streptococcus pneumoniae to the clinical manifestation of invasive pneumococcal disease. Clin Infect Dis. 68: 61–69. ArticlePubMedPDF
- Elberse K, Witteveen S, van der Heide H, van de Pol I, Schot C, et al. 2011. Sequence diversity within the capsular genes of Streptococcus pneumoniae serogroup 6 and 19. PLoS One. 6(9): e25018. ArticlePubMedPMC
- Epping L, van Tonder AJ, Gladstone RA; The Global Pneumococcal Sequencing C, Bentley SD, et al. 2018. SeroBA: rapid high-throughput serotyping of Streptococcus pneumoniae from whole genome sequence data. Microb Genom. 4(7): e000186. ArticlePubMedPMC
- Fani F, Leprohon P, Legare D, Ouellette M. 2011. Whole genome sequencing of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae reveals mutations in penicillin-binding proteins and in a putative iron permease. Genome Biol. 12(11): R115.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G. 2013. Quast: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics. 29(8): 1072–1075. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- Habib M, Porter BD, Satzke C. 2014. Capsular serotyping of Streptococcus pneumoniae using the quellung reaction. J Vis Exp. (84): e51208. Article
- Hudspeth MK, Smith TC, Barrozo CP, Hawksworth AW, Ryan MA, et al. 2001. National department of defense surveillance for invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae: Antibiotic resistance, serotype distribution, and arbitrarily primed polymerase chain reaction analyses. J Infect Dis. 184(5): 591–596. ArticlePubMed
- Jacques LC, Green AE, Barton TE, Baltazar M, Aleksandrowicz J, et al. 2023. Influence of Streptococcus pneumoniae within-strain population diversity on virulence and pathogenesis. Microbiol Spectr. 11(1): e0310322. ArticlePubMedLink
- Joensen KG, Scheutz F, Lund O, Hasman H, Kaas RS, et al. 2014. Real-time whole-genome sequencing for routine typing, surveillance, and outbreak detection of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 52(5): 1501–1510. ArticlePubMedPMCLink
- Johansson MHK, Bortolaia V, Tansirichaiya S, Aarestrup FM, Roberts AP, et al. 2021. Detection of mobile genetic elements associated with antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica using a newly developed web tool: MobileElementFinder. J Antimicrob Chemother. 76(1): 101–109. ArticlePubMedPDF
- Jolley KA, Bray JE, Maiden MCJ. 2018. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 3: 124.ArticlePubMedPMCLink
- Kapatai G, Sheppard CL, Al-Shahib A, Litt DJ, Underwood AP, et al. 2016. Whole genome sequencing of Streptococcus pneumoniae: Development, evaluation and verification of targets for serogroup and serotype prediction using an automated pipeline. PeerJ. 4: e2477. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- Larsen MV, Cosentino S, Rasmussen S, Friis C, Hasman H, et al. 2012. Multilocus sequence typing of total-genome-sequenced bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 50(4): 1355–1361. ArticlePubMedPMCLink
- Lee JT, Li X, Hyde C, Liberator PA, Hao L. 2023. Pfaster: A machine learning-powered serotype caller for Streptococcus pneumoniae genomes. Microb Genom. 9(6): mgen001033.ArticlePubMedPMC
- Lees JA, Harris SR, Tonkin-Hill G, Gladstone RA, Lo SW, et al. 2019. Fast and flexible bacterial genomic epidemiology with poppunk. Genome Res. 29(2): 304–316. ArticlePubMedPMC
- Li Y, Metcalf BJ, Chochua S, Li Z, Gertz RE Jr, et al. 2016. Penicillin-binding protein transpeptidase signatures for tracking and predicting β-lactam resistance levels in Streptococcus pneumoniae. mBio. 7(3): e00756–16. ArticlePubMedPMCLink
- Lo SW, Mellor K, Cohen R, Alonso AR, Belman S, et al. 2022. Emergence of a multidrug-resistant and virulent Streptococcus pneumoniae lineage mediates serotype replacement after PCV13: An international whole-genome sequencing study. Lancet Microbe. 3(10): e735–e743. ArticlePubMedPMC
- Loughran AJ, Orihuela CJ, Tuomanen EI. 2019. Streptococcus pneumoniae: Invasion and inflammation. Microbiol Spectr. 7(2): 10.1128/microbiolspec.gpp3-0004-2018. ArticleLink
- Lu J, Breitwieser FP, Thielen P, Salzberg SL. 2017. Bracken: Estimating species abundance in metagenomics data. Peerj Comput Sci. 3: e104. ArticlePDF
- Oakeson KF, Wagner JM, Mendenhall M, Rohrwasser A, Atkinson-Dunn R. 2017. Bioinformatic analyses of whole-genome sequence data in a public health laboratory. Emerg Infect Dis. 23(9): 1441–1445. ArticlePubMedPMC
- Prjibelski A, Antipov D, Meleshko D, Lapidus A, Korobeynikov A. 2020. Using spades de novo assembler. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 70(1): e102. ArticlePubMedLink
- Rossen JWA, Friedrich AW, Moran-Gilad J, Genomic ESGf, Molecular D. 2018. Practical issues in implementing whole-genome-sequencing in routine diagnostic microbiology. Clin Microbiol Infect. 24(4): 355–360. ArticlePubMed
- Seemann T. 2014. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics. 30(14): 2068–2069. ArticlePubMedPDF
- Sheppard CL, Manna S, Groves N, Litt DJ, Amin-Chowdhury Z, et al. 2022. PneumoKITy: A fast, flexible, specific, and sensitive tool for Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype screening and mixed serotype detection from genome sequence data. Microb Genom. 8(12): mgen000904.ArticlePubMedPMC
- Spanelova P, Jakubu V, Malisova L, Musilek M, Kozakova J, et al. 2020. Whole genome sequencing of macrolide resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A sequence type 416. BMC Microbiol. 20: 224.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- Varghese R, Jayaraman R, Veeraraghavan B. 2017. Current challenges in the accurate identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae and its serogroups/serotypes in the vaccine era. J Microbiol Methods. 141: 48–54. ArticlePubMed
- Weiser JN, Ferreira DM, Paton JC. 2018. Streptococcus pneumoniae: Transmission, colonization and invasion. Nat Rev Microbiol. 16(6): 355–367. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- Wood DE, Lu J, Langmead B. 2019. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 20(1): 257.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- Wyllie AL, Rumke LW, Arp K, Bosch A, Bruin JP, et al. 2016. Molecular surveillance on Streptococcus pneumoniae carriage in non-elderly adults; little evidence for pneumococcal circulation independent from the reservoir in children. Sci Rep. 6: 34888.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- Yan Z, Cui Y, Huang X, Lei S, Zhou W, et al. 2021. Molecular characterization based on whole-genome sequencing of Streptococcus pneumoniae in children living in southwest China during 2017-2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 11: 726740.ArticlePubMedPMC
- Zeng Y, Song Y, Cui L, Wu Q, Wang C, et al. 2023. Phylogenomic insights into evolutionary trajectories of multidrug resistant S. pneumoniae CC271 over a period of 14 years in China. Genome Med. 15(1): 46.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- Zivich PN, Grabenstein JD, Becker-Dreps SI, Weber DJ. 2018. Streptococcus pneumoniae outbreaks and implications for transmission and control: A systematic review. Pneumonia (Nathan). 10: 11.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Genomic analysis and pneumococcal population dynamics across PCV implementation in South Korea, 1997–2023
Jeong-Ih Shin, Sung-Yeon Cho, Jiyon Chu, Chulmin Park, Minho Lee, Joon Young Song, Seung-Hyun Jung, Dong-Gun Lee
Microbial Genomics .2025;[Epub] CrossRef - GPS Pipeline: portable, scalable genomic pipeline for Streptococcus pneumoniae surveillance from Global Pneumococcal Sequencing Project
Harry C. H. Hung, Narender Kumar, Victoria Dyster, Corin Yeats, Benjamin Metcalf, Yuan Li, Paulina A. Hawkins, Lesley McGee, Stephen D. Bentley, Stephanie W. Lo
Nature Communications.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
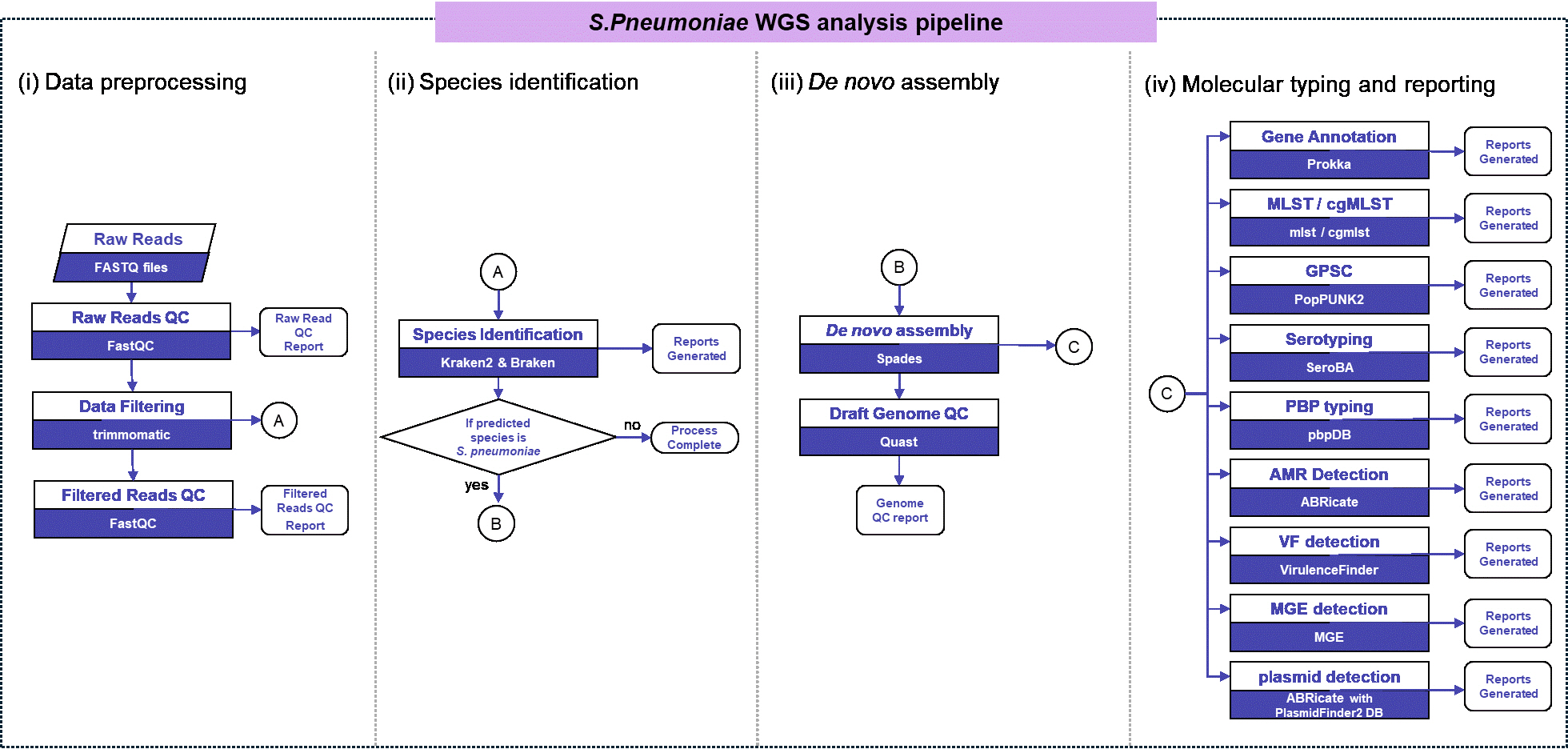
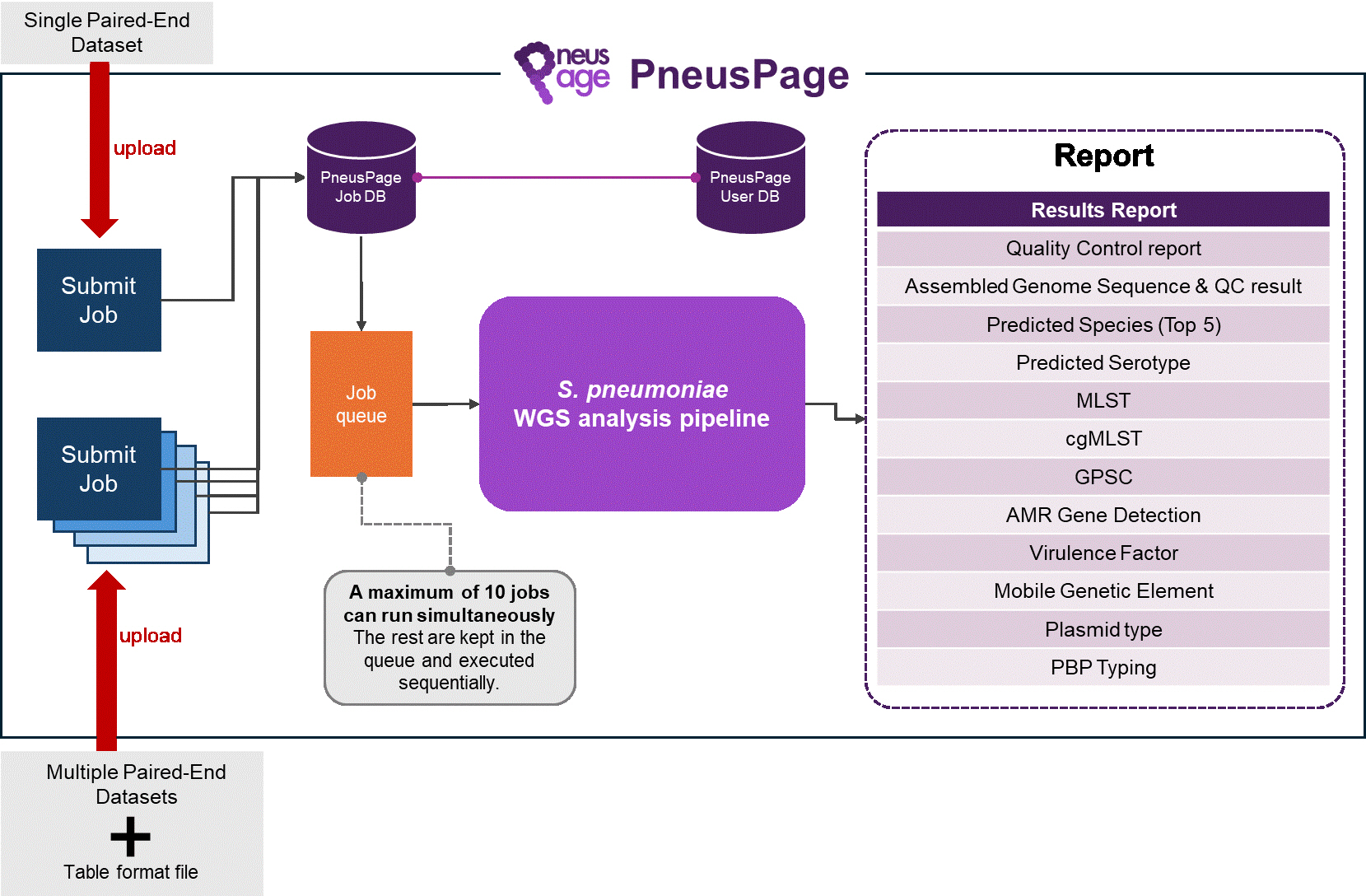
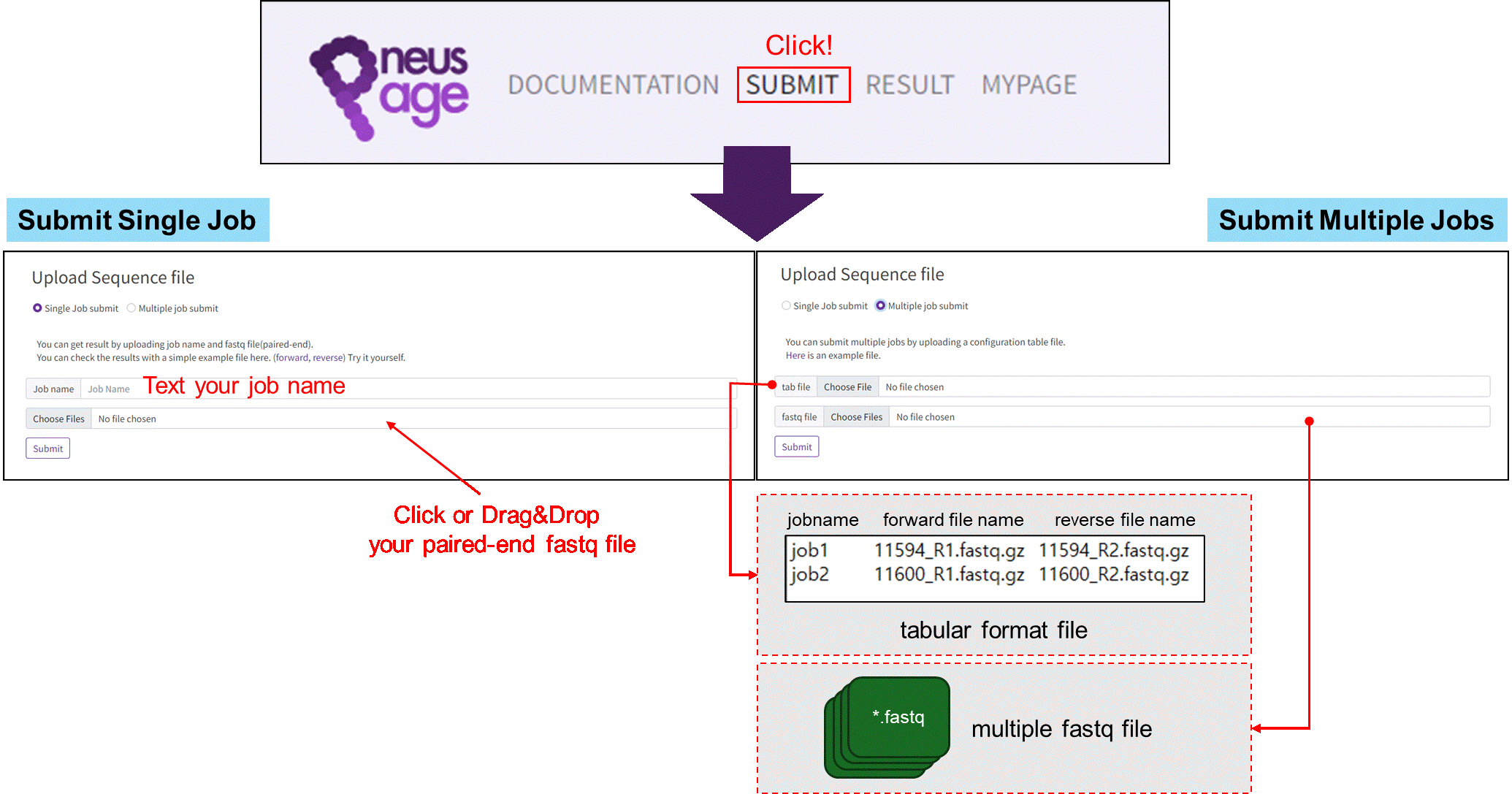
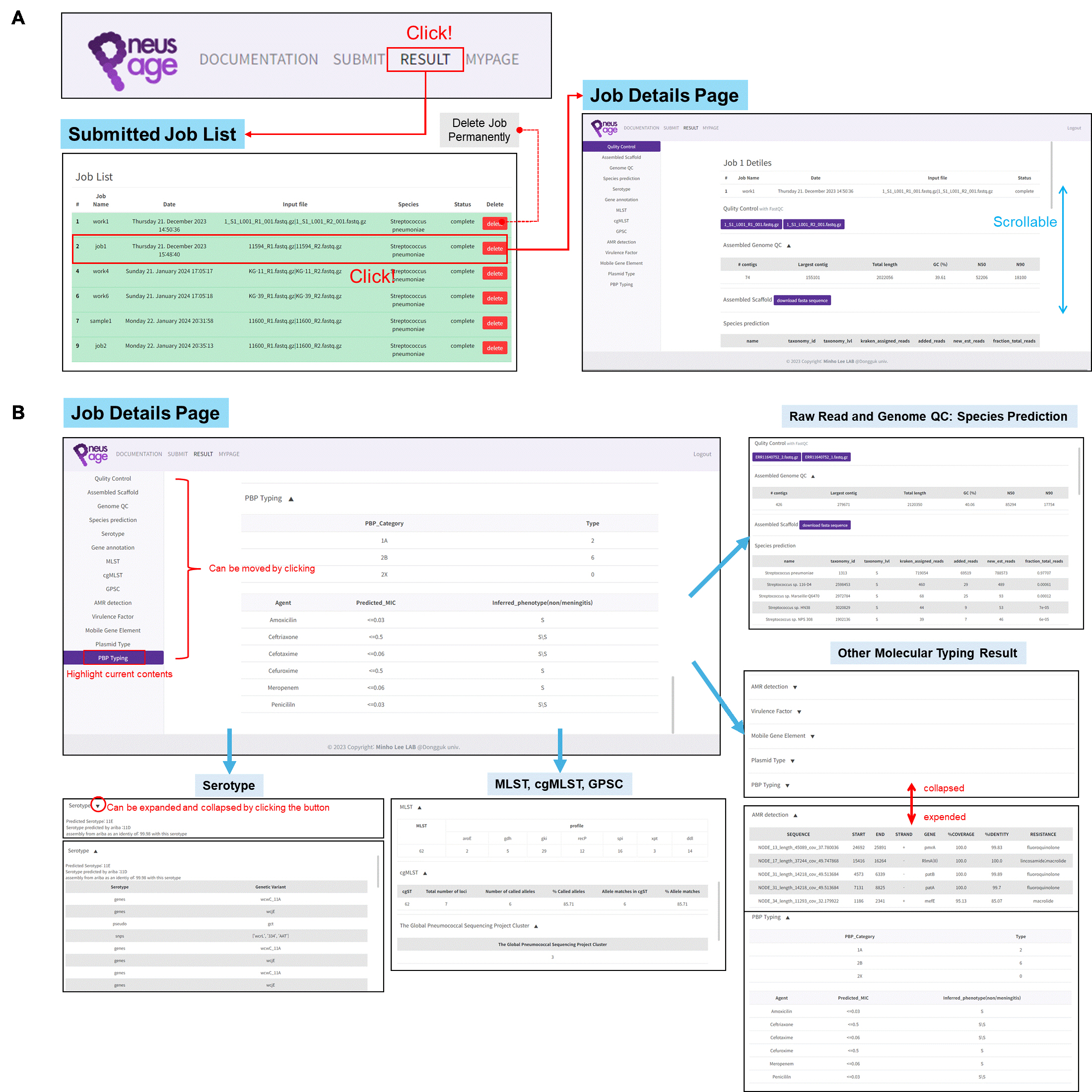
Fig. 1.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 4.
| Category | Subcategory | GPS - PneusPage | GPS - PathogenWatch | PneusPage -PathogenWatch |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serotype | 97.5% (78/80) | 95%(77/80) | 100% (80/80) | |
| MLST | Sequence Type | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) |
| aroE | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | |
| gdh | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | |
| gki | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | |
| recP | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | |
| spi | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | |
| xpt | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | |
| ddl | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | 100% (80/80) | |
| GPSC | 100% (80/80) | 98.75% (79/80) | 98.75% (79/80) | |
| PBP-Typing | pbp1a | 91.25% (73/80) | 98.75% (79/80) | 92.5% (74/80) |
| pbp2b | 95% (76/80) | 100% (80/80) | 95% (76/80) | |
| Pbp2x | 95% (76/80) | 100% (80/80) | 95% (76/80) | |
| pbp1a;pbp2b;pbp2x | 88.75% (71/80) | 98.75% (79/80) | 88.75% (71/80) |
This table presents the concordance rates between the GPS project database samples and two analysis platform, PathogenWatch and PneusPage, across four key
Table 1.
TOP
 MSK
MSK

 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite this Article
Cite this Article





